Server Heat dissipation analysis
Server heat dissipation design is one of the key factors to ensure the stable operation of servers, involving multiple aspects of technologies and strategies. The following is a detailed analysis of server heat dissipation design:
Various Heat Dissipation Design Strategies:
Air-cooled heat dissipation architecture: Servers adopt an air-cooled heat dissipation architecture. By rationally designing heat sinks and matching them with air shrouds, the temperature requirements of various components can be met. For example, high-performance heat pipe heat sinks are used for CPUs, while hard disks are placed at the server's air inlet to utilize the airflow for cooling. Heat pipe heat dissipation: Utilize the high-efficiency heat dissipation ability of heat pipes. Without the need for external power, it relies on the capillary force and vapor pressure difference inside the heat pipe to work and achieve rapid heat dissipation. CPU packaging: TIM (Thermal Interface Material) is used between the CPU chip and the Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS). It has a low melting point and high thermal conductivity, which helps absorb the thermal stress between the chip and the IHS, reducing the temperature gradient and low-temperature hot spots.
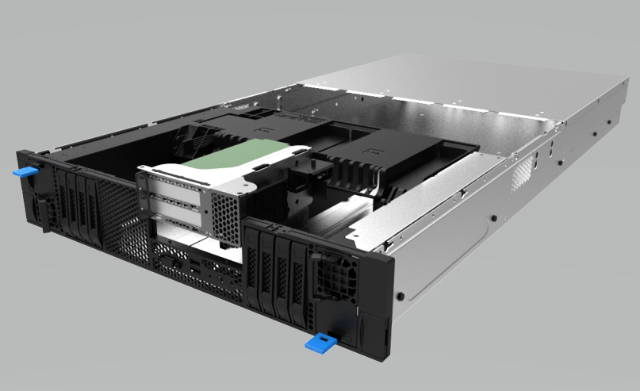
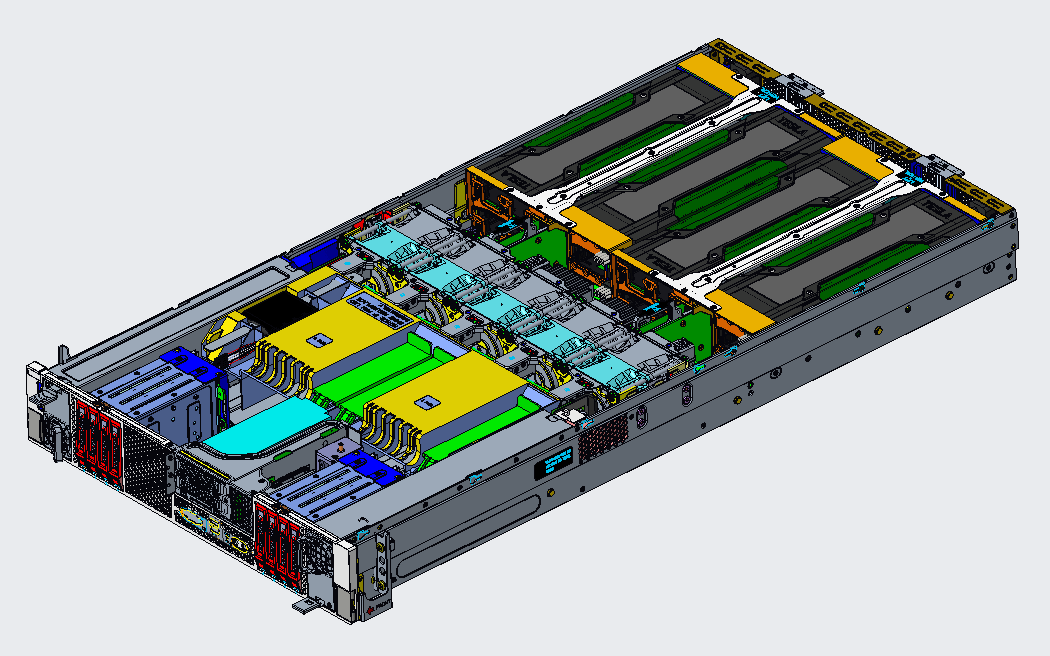
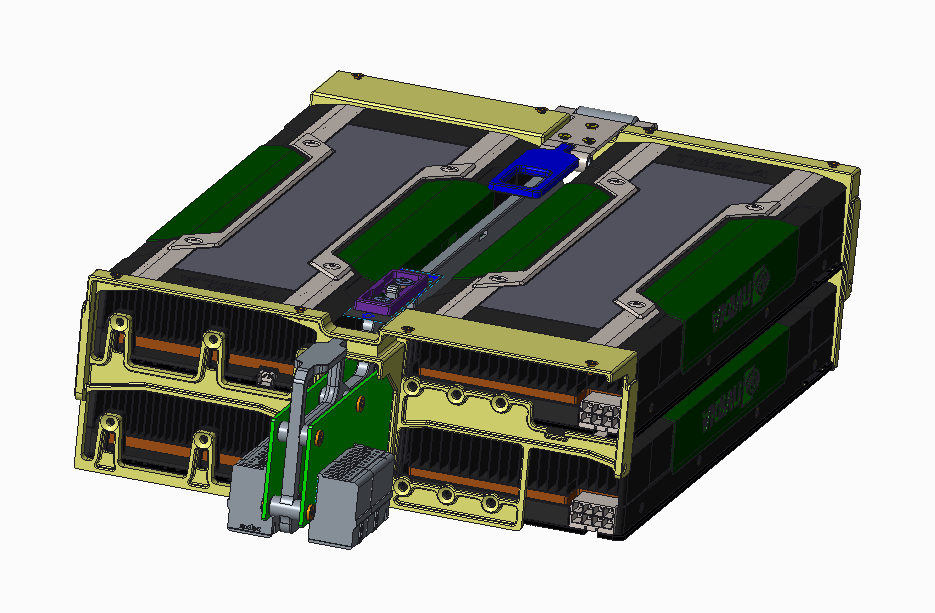
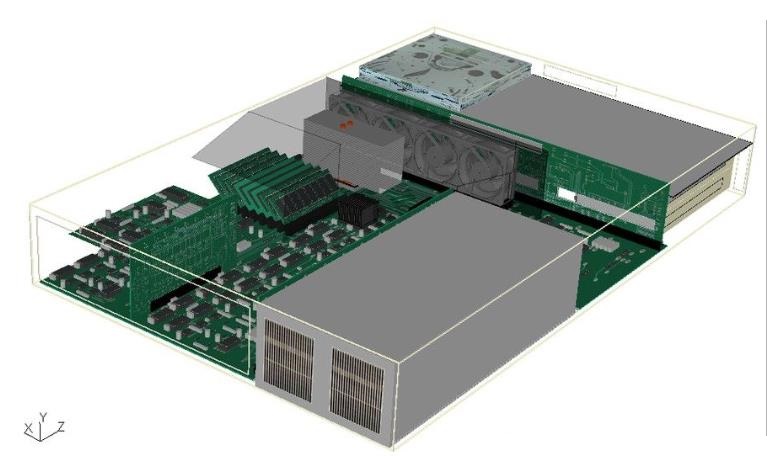
Server Heat Dissipation Simulation Analysis:
Use Flotherm finite element simulation software to conduct simulation analysis on the server. Reasonably divide the mesh and set temperature monitoring points to ensure the accuracy of the simulation results. Through the temperature data after the simulation calculation converges, evaluate the heat dissipation situation of each component to ensure that all components meet the heat dissipation requirements.
This case mainly demonstrates the ability of 6SigmaET to construct models, including air shrouds, inclined DIMMs, Stacked fin heat sinks (with heat pipes), Fan tray, etc. 6SigmaET provides a variety of parametric electronic component databases, making model construction more convenient. The ambient temperature is 20 degrees Celsius, and fan-driven heat dissipation is adopted. Analysis results:
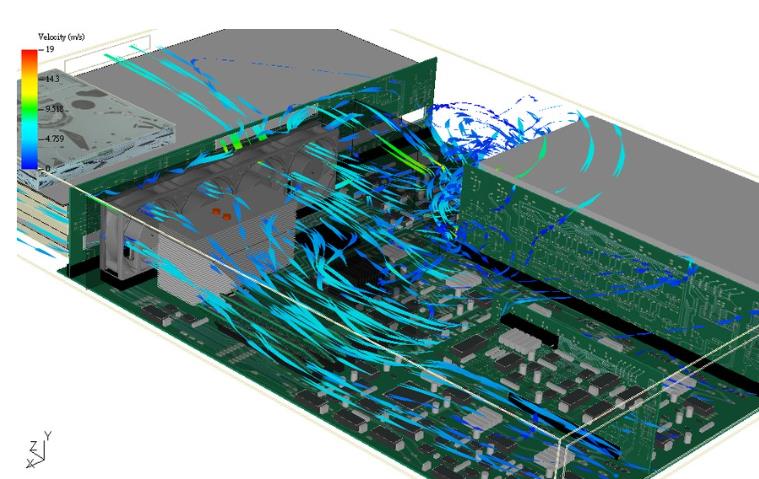
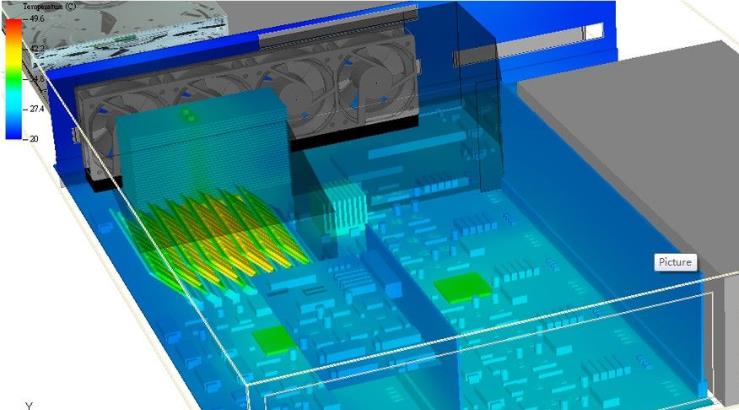
Environmental Control:
Control the temperature and humidity of the environment where the server is located through the air conditioning system, etc., and keep them within an appropriate range to avoid performance degradation or hardware damage caused by overheating. Generally, the temperature in the computer room is controlled between 20 °C and 25 °C, and the humidity is maintained between 40% and 60% RH.
Liquid Cooling Technology:
Cold plate liquid cooling system: Although it has relatively high costs, including hardware costs and hidden costs, it can effectively reduce the internal temperature of the server and improve the heat dissipation effect. However, the large-scale commercial application of liquid cooling technology faces challenges such as compatibility and cost. Immersion liquid cooling technology: Replace the working medium used for server heat dissipation from air to an insulating liquid. The system is simple and has high reliability. However, it also faces compatibility and cost issues, especially the reconstruction of the server architecture and the increase in operation and maintenance costs.
In summary, server heat dissipation design involves multiple aspects of technologies and strategies, including air-cooled heat dissipation architecture, heat pipe heat dissipation, CPU packaging technology, simulation analysis, environmental control, and the application of liquid cooling technology. Each technology has its own advantages and limitations, and it is necessary to select an appropriate heat dissipation solution according to the specific requirements and operating environment of the server.

Leto Intelligent Manufacturing Technology (Suzhou) Co., LTD
199 4191 2022
Business consulting/technical consulting/exchange advice
Scan code wechat consultation, 24 hours to look forward to your voice

